[nuxt】Nuxt的生命周期
官网的生命周期介绍: Nuxt Lifecycle
我们结合Vue的生命周期钩子来理解。
画了一张图便于理解:
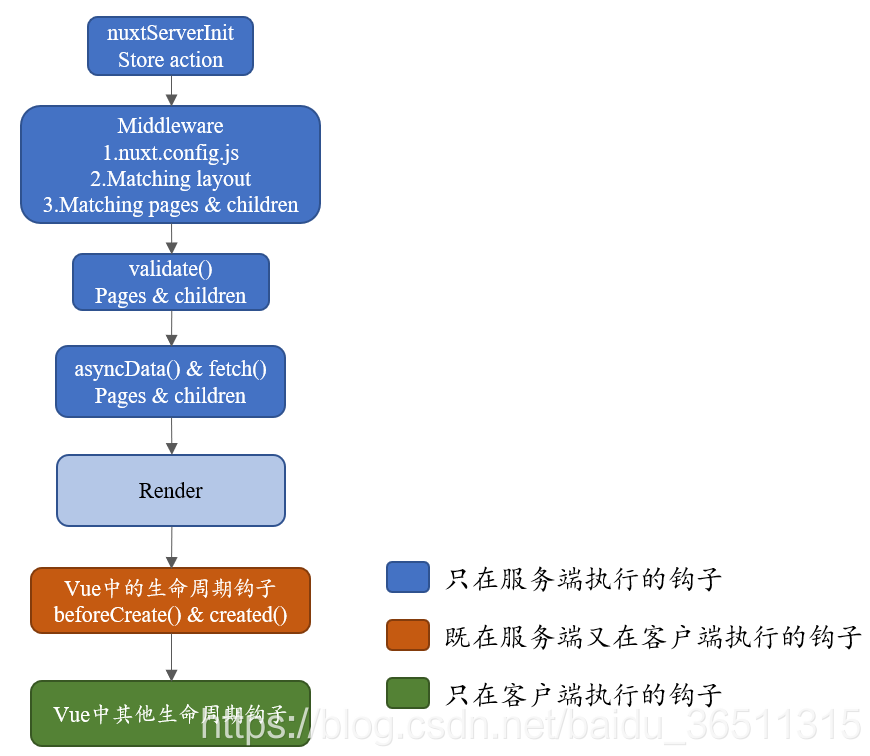
- nuxtServerInit 服务端初始化
- middleware 中间件运行
- ·validate()·校验参数
- asyncData() & fetch() 异步数据处理
- Render 客户端开始渲染
1.nuxtServerInit
在s t o r e \color{FF7D00}{store}store目录下新建i n d e x . j s \color{FF7D00}{index.js}index.js,并写入以下内容:
export const actions = {
nuxtServerInit(store, context) {
// 可以在这里初始一些内容到store中
console.log('nuxtServerInit!!!');
}
};
npm run dev启动项目。
启动成功后,我们访问一下http://localhost:3000/页面。然后看服务端打印的内容:
√ Client
Compiled successfully in 2.54s
√ Server
Compiled successfully in 2.17s
i Waiting for file changes 11:12:40
i Memory usage: 171 MB (RSS: 245 MB) 11:12:40
i Listening on: http://localhost:3000/ 11:12:40
nuxtServerInit!!!
这说明我们写在s t o r e / i n d e x . j s \color{FF7D00}{store/index.js}store/index.js中的n u x t S e r v e r I n i t \color{FF7D00}{nuxtServerInit}nuxtServerInit方法在页面加载时被自动调用
2.middleware
middleware的执行顺序:nuxt.config.js中配置的 -> 匹配layouts -> 匹配pages
在middleware{middleware}middleware目录下新建f i l t e r . j s \color{FF7D00}{filter.js}filter.js,并写入以下内容:
export default ({ store, route, redirect, params, query, req, res }) => {
// context 服务端上下文
console.log('middleware nuxt.config.js !!!');
}在 nuxt.config.js{nuxt.config.js}nuxt.config.js中插入内容:
router: {
middleware: 'filter'
},
注:修改了配置文件需要重启才能生效。
修改layouts{layouts}layouts目录下的d e f a u l t . v u e \color{FF7D00}{default.vue}default.vue:
<template>
<div>
<nuxt />
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
// middleware: 'filter' // 可指向在nuxt.config.js中配置的中间件
middleware() {
console.log('middleware layouts!!!');
},
data () {
return {
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
修改pages目录下的index.vue,新增内容:
...
<script>
export default {
// middleware: 'filter' // 可指向在nuxt.config.js中配置的中间件
middleware() {
console.log('middleware pages!!!');
},
}
</script>
重新请求http://localhost:3000/页面。然后看服务端打印的内容:
nuxtServerInit!!!
middleware nuxt.config.js !!!
middleware layouts!!!
middleware pages!!!
应证了前面提到的,middleware的执行顺序:
nuxt.config.js中配置的 -> 匹配layouts -> 匹配pages。
我们可以在中间件中获取服务端的上下文context,做些操作:
middleware(context) {
// 用context进行一些操作
},
3.validate
修改pages目录下的index.vue,新增内容:
...
<script>
export default {
...
// 路由发生变化时,做参数校验
validate({params, query}) {
// 进行一些校验操作
console.log('validate!!!');
return true;
}
}
</script>重新请求http://localhost:3000/页面。然后看服务端打印的内容:
nuxtServerInit!!!
middleware nuxt.config.js !!!
middleware layouts!!!
middleware pages!!!
validate!!! 如果我们让validate()返回false,重新请求http://localhost:3000/页面:
服务端正常打印信息。
但是,客户端页面会提示所访问的页面不存在。
4.asyncData 和 fetch
页面首次加载时,异步数据的获取代码可写在这两个钩子里面(不能写在Vue的created或者mounted里面,页面获取不到)。
修改pages目录下的index.vue,新增内容:
...
<script>
export default {
...
validate({params, query}) {
// 进行一些校验操作
console.log('validate!!!');
return true;
},
asyncData(context){
console.log('asyncData');
return {
a: 2000
}
},
data() {
return {
b: 1000
};
},
fetch({store}){
console.log('fetch');
}
}
</script>
重新请求http://localhost:3000/页面。然后看服务端打印的内容:
nuxtServerInit!!!
middleware nuxt.config.js !!!
middleware layouts!!!
middleware pages!!!
validate!!!
asyncData
fetch 客户端界面,我们通过Vue Devtools查看页面的数据store:
5.beforeCreate 和 created
修改pages目录下的index.vue,新增内容:
...
<script>
export default {
...
// 客户端和服务端
beforeCreate() {
console.log('beforeCreate');
},
created() {
console.log('created');
},
}
</script>重新请求http://localhost:3000/页面。可以看到服务端打印的内容:
nuxtServerInit!!!
middleware nuxt.config.js !!!
middleware layouts!!!
middleware pages!!!
validate!!!
asyncData
fetch
beforeCreate
created 客户端打印的内容:
beforeCreate
created Vue中的其他生命周期钩子
修改pages目录下的index.vue,新增内容:
...
<script>
export default {
...
beforeMount() {
console.log('beforeMount');
},
mounted() {
console.log('mounted');
},
beforeUpdate() {
console.log('beforeUpdate');
},
updated() {
console.log('updated');
},
beforeDestroy() {
console.log('beforeDestroy');
},
destroyed() {
console.log('destroyed');
}
}
</script>注: 服务端渲染不支持 activated 和 deactivate,因此Vue中的这两个生命周期钩子无效。
其他生命周期钩子仅在客户端运行。
总结,在服务端的生命周期钩子中,只能通过context去访问服务端的上下文环境,服务端中的this指向的是undefined,不存在window对象。